Understanding the Connection Between Breathing, Anxiety, and Sleep
The Physiology of Anxiety and Sleep Disruption
Many individuals struggle with anxiety, which can significantly impact sleep quality. Anxiety triggers an activation of the body’s stress response, leading to physiological changes such as increased heart rate and muscle tension. These changes often cause restlessness and difficulty falling or staying asleep. Over time, chronic stress and anxiety can disrupt the natural balance of the nervous system, contributing to persistent sleep problems. Understanding this physiological link is essential to appreciating why managing breath can be a powerful tool in reducing anxiety and improving sleep patterns.

How Breathing Influences the Nervous System
Breathing plays a vital role in regulating the nervous system, especially the balance between the sympathetic “fight or flight” response and the parasympathetic “rest and digest” system. When under stress, people tend to take shallow breaths using the muscles of the neck and chest, which can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and restlessness. In contrast, slow, deep breathing stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and helping to calm both the mind and body. This calming influence aids in reducing anxiety symptoms and facilitating better sleep quality by encouraging a state conducive to rest.
Top Breathing Techniques to Alleviate Anxiety
Diaphragmatic Breathing: Basics and Benefits
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, involves engaging the diaphragm to take slower, deeper breaths. This technique encourages oxygen to flow deeply into the lungs, which helps reduce muscle tension and promote mental calmness. Starting by placing one hand on the abdomen and the other on the chest, you focus on allowing the belly to rise and fall with each breath, ensuring that the chest remains relatively still. This method can effectively counterbalance the shallow upper-chest breathing commonly triggered by stress, thereby reducing anxiety symptoms over time.
4-7-8 Breathing Technique for Relaxation
The 4-7-8 breathing approach offers a structured rhythm for promoting relaxation and anxiety relief. It involves inhaling quietly through the nose for a count of four seconds, holding the breath for seven seconds, then exhaling slowly through the mouth for eight seconds. This deliberate pacing helps to lengthen exhalation, which is known to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and induce a calming effect. Regular practice can improve one’s ability to manage anxiety and create a more peaceful mental state.
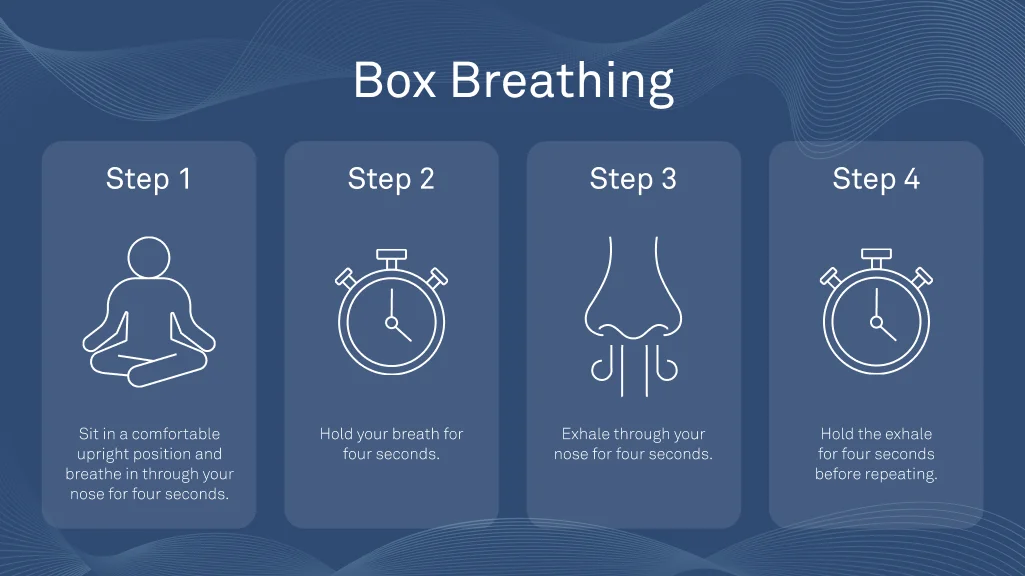
Box Breathing for Mental Clarity
Box breathing, sometimes called square breathing, entails inhaling, holding, exhaling, and holding the breath again, each for a count of four seconds. This simple yet powerful pattern promotes focused awareness on the breath, which can help reduce distracting thoughts and stress responses. Its balanced timing fosters a sense of mental clarity and calmness, making it an effective tool for managing moments of heightened anxiety and regaining composure throughout the day.
Breathing Exercises to Enhance Sleep Quality
Progressive Muscle Relaxation with Breathing
Combining progressive muscle relaxation with controlled breathing can support the transition into restful sleep. This method involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups progressively while maintaining slow, deep breaths. Coordinating these actions helps release physiological tension that might interfere with falling asleep. The breathing calms the nervous system, while muscle relaxation prepares the body physically for rest, working together to improve overall sleep quality.
Guided Breath Awareness for Falling Asleep Faster
Guided breath awareness involves focusing attention solely on the natural flow of the breath, often paired with calming mental imagery. By tuning into the sensation of breathing in and out, the mind gradually detaches from anxious or racing thoughts, creating a conducive environment for sleep onset. If visualization proves difficult, utilizing audio resources such as podcasts or videos that guide breath and imagery can enhance the experience. This technique encourages relaxation and reduces sleep latency, helping individuals fall asleep more quickly.
Incorporating Breathing Exercises Into Your Daily Routine
Morning vs. Evening Breathing Practices
Integrating breathing exercises into both morning and evening routines can provide distinct benefits. Morning sessions often focus on energizing and centering the mind for the day ahead, using techniques that promote focus and mental clarity, like box breathing. Evening practices, on the other hand, concentrate on relaxation to unwind from daily stressors, preparing the body and mind for restful sleep. Selecting the right timing and type of breathing exercises allows for a balanced approach that supports anxiety management throughout the day and better sleep at night.
Creating a Personalized Breathing Schedule
Personalizing a breathing schedule increases the likelihood of consistent practice, which is key to experiencing long-term benefits. Start by setting aside dedicated time, ideally five minutes or more, for daily sessions. Tailor the frequency and techniques to fit personal preferences and lifestyle. For example, some may find practicing diaphragmatic breathing three times a day helpful, while others might prefer a single longer evening session. Flexibility coupled with commitment encourages the establishment of a sustainable and effective breathing routine.
Potential Challenges and Tips for Success
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
A few common pitfalls can hinder progress with breathing exercises. One major mistake is taking shallow breaths using neck and chest muscles instead of fully engaging the diaphragm. This limits the calming effect and may even increase anxiety. Another frequent error is expecting immediate results without consistent practice, which leads to discouragement. Additionally, skipping regular practice or using sessions that are too short—less than five minutes—or too fast can reduce effectiveness. Avoiding extensive standing during practice and minimizing interruptions are also important for maintaining focus. Ensuring proper training and comfort during exercises supports better outcomes, especially with more technical techniques.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Techniques
Monitoring how breathing exercises impact anxiety levels and sleep quality helps guide adjustments for optimal benefit. Keeping a simple journal or using a tracking app can record session frequency, duration, and effects experienced. Over time, this data can highlight which techniques resonate most and when improvements occur. If progress plateaus, experimenting with varying the timing, switching breathing methods, or incorporating guided support may be useful. Regular reflection alongside persistence encourages a mindful and adaptive approach to managing anxiety and improving sleep through breathing.

